Network IPv4 Class Category A B C D and E all Five Types of Network Classes
Series 1/Part 3 : Networking Classes
आइये जानते हे नेटवर्किंग क्लासेज क्या हे और इसकी क्यों जरुरत पड़ी -
Very Very Important Topic Read Carefully for Exam point of view
Let us know about Networking classes
What
are IP classes and how can you identify the IP class of given an IP address?
Currently there are three classes of TCP/IP networks. Each class uses the 32-bit IP address space differently, providing more or fewer bits for the network part of the address.
These classes are class A, class B, and class C.
Further Note :- An IP address has 4
sets (octets) of numbers each with a value up to 255.
For Example, the range of the home or commercial connection started
primarily between 190 x or 10 x. IP classes are differentiated based on the
number of hosts it supports on a single network. If IP classes support more
networks then very few IP addresses are available for each network.
There are three types
of IP classes and are based on the first octet of IP addresses which are
classified as Class A, B or C. If the first octet begins with 0 bit then it is
of type Class A.
Class A type has a range up to 127.x.x.x (except 127.0.0.1). If it starts with bits 10 then it belongs to
A class A network number uses the first eight bits of the IP address as its "network part." The remaining 24 bits comprise the host part of the IP address.
The values assigned to the first byte of class A network numbers fall within the range 0-127. Consider the IP address 72.5.10.4. The value 72 in the first byte indicates that the host is on a class A network that shown in blue line area . The remaining bytes, 5.10.4, establish the host address that shown in Red line area. The Inter NIC assigns only the first byte of a class A number. Use of the remaining three bytes is left to the discretion of the owner of the network number. Only 127 class A networks can exist. Each one of these numbers can accommodate up to 16,777,214 hosts.
Public IP Range: 1.0.0.0 to 127.0.0.0
First octet value range from 1 to 127

- Private IP Range: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- Subnet Mask: 255.0.0.0 (8 bits)
- Number of Networks: 126
- Number of Hosts per Network: 16,777,214
- 2^7-2= 126 network ID(Here 2 address is subtracted because 0.0.0.0 and 127.x.y.z are special address. )
- 2^24 – 2 = 16,777,214 host ID
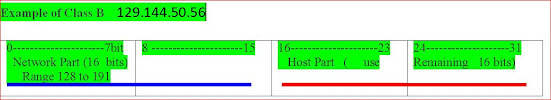
Class B. having a range from 128.x to 191.x. IP class belongs to
- Public IP Range: 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.0.0
- Private IP Range: 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0 (16 bits)
- Number of Networks: 16,382
- Number of Hosts per Network: 65,534
- 2^14 = 16384 network address
- 2^16 – 2 = 65534 host address
Class C . has a range from
192.x to 223.x.
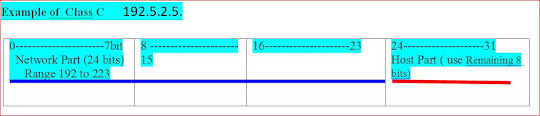
Class C network numbers use 24 bits for the network number and 8 bits for host numbers. Class C network numbers are appropriate for networks with few hosts--the maximum being 254. A class C network number occupies the first three bytes of an IP address. Only the fourth byte is assigned at the discretion of the network owners.
The first byte of a class C network number covers the range 192-223. The second and third each cover the range 1- 255. A typical class C address might be 192.5.2.5. The first three bytes, 192.5.2, form the network number. The final byte in this example, 5, is the host number.
- Public IP Range: 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.0
- Private IP Range: 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
- Special IP Range: 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.255
- Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 (24 bits)
- Number of Networks: 2,097,150
- Number of Hosts per Network: 254
Table graphically represents the bytes in a class C address.
- 2^21 = 2097152 network address
- 2^8 – 2 = 254 host address
Note:- Classes D and E are reserved for multicast and experimental purposes respectively.
Class D
For Class D, IP addresses are not allocated to hosts and are used for multicasting. Multicasting allows a single host to send a single stream of data to thousands of hosts across the Internet at the same time. It is often used for audio and video streaming,Use of Class D in Ip based cable TV networks. Another example is the delivery of real-time stock market data from one source to many brokerage companies.
- Range: 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
- First octet value range from 224 to 239
- Number of Networks: N/A
- Number of Hosts per Network: Multicasting
Class E
For Class E, IP addresses are not allocated to hosts and are not available for general use. These are reserved for research purposes.
- Range: 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
- First octet value range from 240 to 255
- Number of Networks: N/A
- Number of Hosts per Network: Research/Reserved/Experimental
Private IP Addresses
Within each network class, there are designated IP address that is reserved specifically for private/internal use only. This IP address cannot be used on Internet-facing devices as that are non-routable.
For example, web servers and
FTP servers must use non-private IP addresses. However, within your own home or
business network, private IP addresses are assigned to your devices (such as
workstations, printers, and file servers).
- Class A Private Range: 10.0.0.0 to
10.255.255.255
- Class B Private APIPA Range: 169.254.0.0
to 169.254.255.255
- Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) is a feature with Microsoft Windows-based computers to automatically assign itself an IP address within this range
- if a Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) server is not available on the network.
A DHCP server is a network device that is responsible for assigning IP
addresses to devices on the network.
At your home, your Internet modem or router likely provides this functionality. In your work place, a Microsoft Windows Server, a network firewall, or some other specialized network device likely provides this functionality for the computer at your work environment. - Class B Private Range: 172.16.0.0 to
172.31.255.255
- Class C Private Range: 192.168.0.0 to
192.168.255.255
Special Purpose IP Addresses
- IP Range: 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.255 are network testing addresses (also referred to as loop-back addresses). These are virtual IP address, in that they cannot be assigned to a device. Specifically, the IP 127.0.0.1 is often used to troubleshoot network connectivity issues using the ping command Specifically, it tests a computer's TCP/IP network software driver to ensure it is working properly or not.

Comments